| Tokyo Institute of Technology Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Science
and Engineering Department of Materials Science and Engineering |
|
| Kumai Laboratory | |
| Tokyo Institute of Technology Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Science
and Engineering Department of Materials Science and Engineering |
|
| Kumai Laboratory | |
Magnetic pulse welding (MPW) is one of the impact solid-state welding methods.
When metal plates collide obliquely at high
speed, such as several hundreds of meters per second, the interface layer of the plate is emitted as metal jet. Consequently,
atoms on the cleaned surface establish strong metallurgical bond. This
process is achieved at a few microseconds. This method
is adaptive for wide variety of similar- and dissimilar- combinations
of metals.
We have researched magnetic pulse welding for several years. Figure 1 shows
the schematic illustration of magnetic pulse
welding. In magnetic pulse welding, flyer plate deforms partially at high speed by Fleming’s left-hand law, and collides into parent
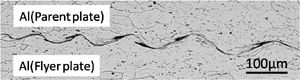
plate. The weld interface shows wavy morphology (Figure 2), and the region
along the weld interface is composed of amorphous
layer and ultrafine grains. Multilayer lap joints of Al plates (Figure
3) and metal-metallic glass lap joints were also fabricated by
this method.
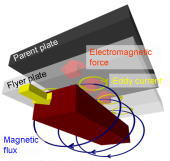 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of magnetic pulse welding |
 |
(a) |
|
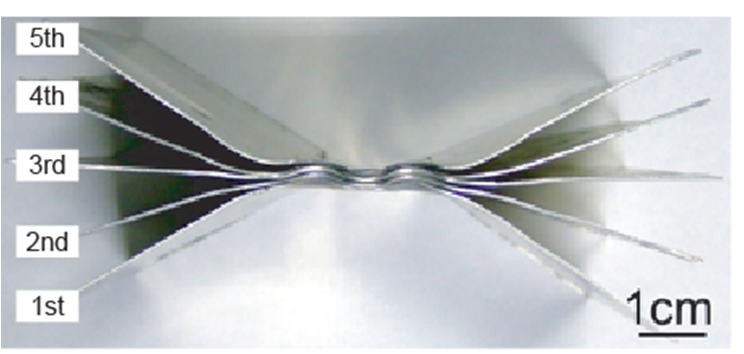 Fig.3 Multilayered lap joint of Al plates |
 (b) |
| Fig.2 Weld interface(Al:Al/Ni, b:Al/Al) |
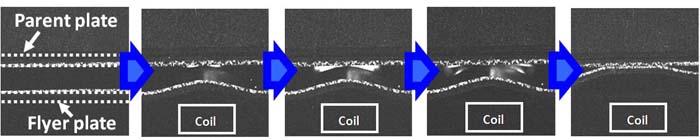
We currently research on the characteristic weld interface morphology and
the metal jet emission behavior in several similar-
and dissimilar- impact welded lap joining from both by numerical analysis and experimental methods. The chemical components of
metal jet are also investigated.
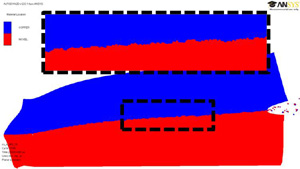
Fig.5 The metal jet emision and the wavy interface produced in simulation
BACK
![]()